吲哚菁绿ICG叠氮化物
 |
货号 |
985 |
存储条件 |
在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 |
1 mg |
价格 |
2544 |
| Ex (nm) |
789 |
Em (nm) |
814 |
| 分子量 |
799.05 |
溶剂 |
DMSO |
| 产品详细介绍 |
简要概述
产品基本信息
货号:985
产品名称:吲哚菁绿ICG叠氮化物
规格:1mg
储存条件:-15℃避光防潮
保质期:12个月
产品物理化学光谱特性
分子量:799.05
外观:固体
溶剂:DMSO
激发波长(nm):780
发射波长(nm):800
产品介绍
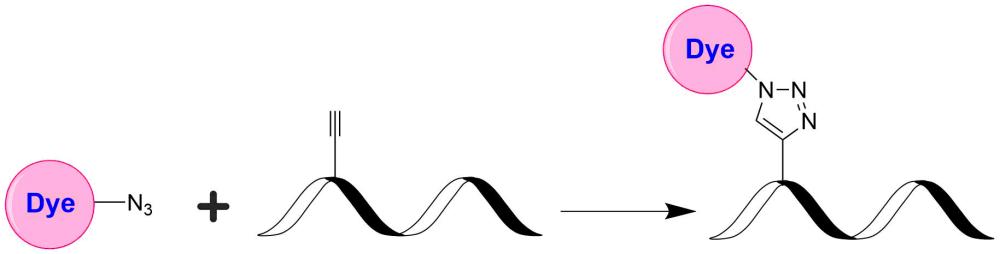
吲哚菁绿(ICG)是一种三碳菁型染料,具有NIR吸收特性(峰值吸收约780 nm),最大发射波长约为800 nm。FDA批准了非侵入性近红外(NIR)荧光成像染料ICG进行眼科血管造影,以确定心输出量以及肝血流量和功能。由于红外频率穿透视网膜层,因此与荧光素血管造影相比,ICG血管造影可以成像更深的循环模式。 ICG与血浆蛋白紧密结合,并局限于血管系统。 ICG的半衰期为150到180秒,只能从肝脏转移至胆汁而从循环系统中移除。最近的一项研究表明,ICG可在注射后20分钟内靶向动脉粥样硬化,并为体内检测动脉粥样硬化兔中富含脂质,发炎,冠状动脉粥样斑块提供了足够的信号增强。离体荧光反射成像显示,与注射盐水的带有粥样斑块的兔子相比,注射了ICG的带有粥样斑块的兔子的斑块靶标与背景比率高。它还可用于其他医学诊断和癌症患者中,用于实体瘤的检测,淋巴结的定位以及在重建手术期间的血管造影,视网膜和脉络膜血管的可视化以及光动力疗法。在癌症诊断和治疗中,ICG既可以用作显像染料又可以用作热疗剂。在可见光范围内几乎没有吸收,这是由于低自发荧光,组织吸收和在近红外波长(700-900 nm)下的散射引起的。这种ICG叠氮化物可用于通过众所周知的点击化学化学选择性标记炔烃标记的生物分子(如蛋白质,脂质,核酸,糖)。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的吲哚菁绿ICG叠氮化物。
点击查看光谱
参考文献
Assessment of Lexiscan for Blood Brain Barrier disruption to facilitate Fluorescence brain imaging
Authors: Pak, Rebecca W and Le, Hanh and Valentine, Heather and Thorek, Daniel and Rahmim, Arman and Wong, Dean and Kang, Jin U
Journal: (2017): ATu3B–2
Bioengineering of injectable encapsulated aggregates of pluripotent stem cells for therapy of myocardial infarction
Authors: Zhao, Shuting and Xu, Zhaobin and Wang, Hai and Reese, Benjamin E and Gushchina, Liubov V and Jiang, Meng and Agarwal, Pranay and Xu, Jiangsheng and Zhang, Mingjun and Shen, Rulong and others
Journal: Nature Communications (2016): 13306
Deep Photoacoustic/Luminescence/Magnetic Resonance Multimodal Imaging in Living Subjects Using High-Efficiency Upconversion Nanocomposites
Authors: Liu, Yu and Kang, Ning and Lv, Jing and Zhou, Zijian and Zhao, Qingliang and Ma, Lingceng and Chen, Zhong and Ren, Lei and Nie, Liming
Journal: Advanced Materials (2016)
Single-Layer MoS2 Nanosheets with Amplified Photoacoustic Effect for Highly Sensitive Photoacoustic Imaging of Orthotopic Brain Tumors
Authors: Chen, Jingqin and Liu, Chengbo and Hu, Dehong and Wang, Feng and Wu, Haiwei and Gong, Xiaojing and Liu, Xin and Song, Liang and Sheng, Zonghai and Zheng, Hairong
Journal: Advanced Functional Materials (2016)
A simple and effective technique for identification of intersegmental planes by infrared thoracoscopy after transbronchial injection of indocyanine green
Authors: Sekine Y, Ko E, Oishi H, Miwa M.
Journal: J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2012)
Adverse Reaction in Patients with Drug Allergy History After Simultaneous Intravenous Fundus Fluorescein Angiography and Indocyanine Green Angiography
Authors: Su Z, Ye P, Teng Y, Zhang L, Shu X.
Journal: J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. (2012)
An innovative method for detecting surgical errors using indocyanine green angiography during carotid endarterectomy: a preliminary investigation
Authors: Lee CH, Jung YS, Yang HJ, Son YJ, Lee SH.
Journal: Acta Neurochir (Wien) (2012): 67
Anatomic response of occult choroidal neovascularization to intravitreal ranibizumab: a study by indocyanine green angiography
Authors: Querques G, Tran TH, Forte R, Querques L, B and ello F, Souied EH.
Journal: Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2012): 479
Applicability of radiocolloids, blue dyes and fluorescent indocyanine green to sentinel node biopsy in melanoma
Authors: Uhara H, Yamazaki N, Takata M, Inoue Y, Sakakibara A, Nakamura Y, Suehiro K, Yamamoto A, Kamo R, Mochida K, Takenaka H, Yamashita T, Takenouchi T, Yoshikawa S, Takahashi A, Uehara J, Kawai M, Iwata H, Kadono T, Kai Y, Watanabe S, Murata S, Ikeda T, Fukamizu H, Tanaka T, Hatta N, Saida T.
Journal: J Dermatol (2012): 336
Application of indocyanine green videoangiography in surgery for spinal vascular malformations
Authors: Misra BK, Pur and are HR.
Journal: J Clin Neurosci. (2012)