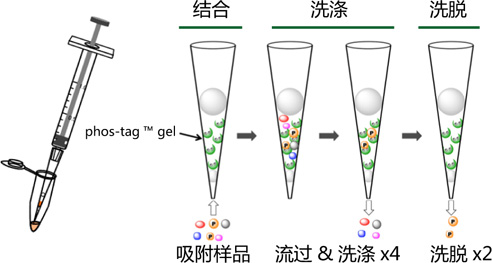
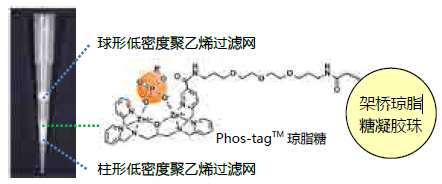
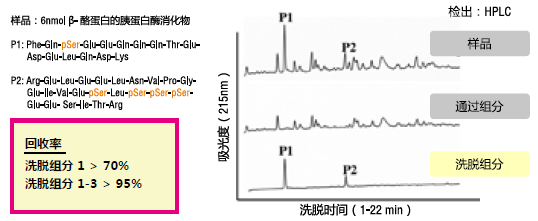
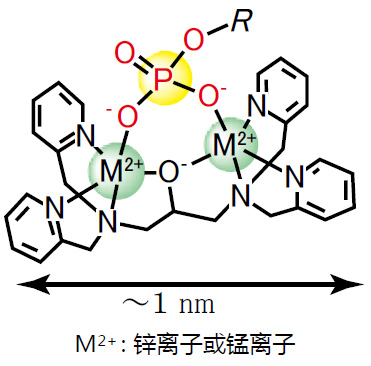
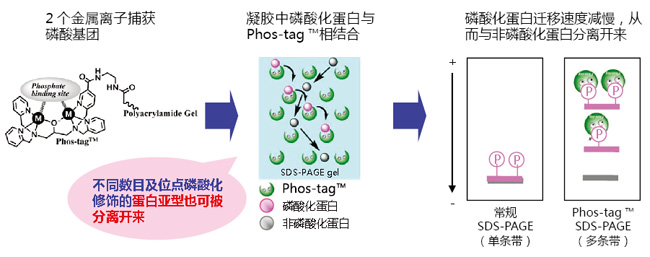
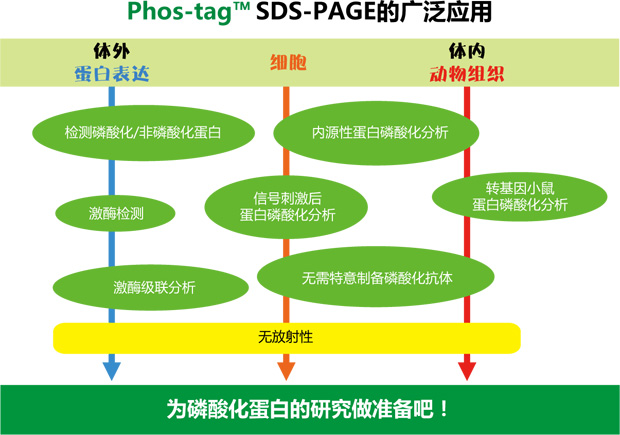
【参考文献】
· Conversion of graded phosphorylation into switch-like nuclear translocation via autoregulatory mechanisms in ERK signalling[J].Nature communications, 2016, 7,Shindo Y, Iwamoto K, Mouri K, et al.
· PTEN modulates EGFR late endocytic trafficking and degradation by dephosphorylating Rab7[J]. Nature communications, 2016, 7,Shinde S R, Maddika S.
· Feedback control of ErbB2 via ERK-mediated phosphorylation of a conserved threonine in the juxtamembrane domain[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 31502,Kawasaki Y, Sakimura A, Park C M, et al.
· Plastid-nucleus communication involves calcium-modulated MAPK signalling[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7,Guo H, Feng P, Chi W, et al.
· Sequential domain assembly of ribosomal protein S3 drives 40S subunit maturation[J]. Nature communications, 2016, 7,Mitterer V, Murat G, Réty S, et al.
· Phos-tag analysis of Rab10 phosphorylation by LRRK2: a powerful assay for assessing kinase function and inhibitors[J]. Biochemical Journal, 2016: BCJ20160557,Ito G, Katsemonova K, Tonelli F, et al.
· Analysis of phosphorylation of the myosin targeting subunit of smooth muscle myosin light chain phosphatase by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE[J]. The FASEB Journal, 2016, 30(1 Supplement): 1209.1-1209.1,Walsh M P, MacDonald J A, Sutherland C.
· Using Phos-Tag in Western Blotting Analysis to Evaluate Protein Phosphorylation[J]. Kidney Research: Experimental Protocols, 2016: 267-277,Horinouchi T, Terada K, Higashi T, et al.
· The Abundance of Nonphosphorylated Tau in Mouse and Human Tauopathy Brains Revealed by the Use of Phos-Tag Method[J]. The American journal of pathology, 2016, 186(2): 398-409,Kimura T, Hatsuta H, Masuda-Suzukake M, et al.
· Phos-tag SDS-PAGE resolves agonist-and isoform-specific activation patterns for PKD2 and PKD3 in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2016,Qiu W, Steinberg S F.
· Analysis of phosphorylation of the myosin-targeting subunit of myosin light chain phosphatase by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 2016, 310(8): C681-C691,Sutherland C, MacDonald J A, Walsh M P.
· Electrochemical biosensor for protein kinase A activity assay based on gold nanoparticles-carbon nanospheres, phos-tag-biotin and β-galactosidase[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, 86: 508-515,Zhou Y, Yin H, Li X, et al.
· Validation of Cis and Trans Modes in Multistep Phosphotransfer Signaling of Bacterial Tripartite Sensor Kinases by Using Phos-Tag SDS-PAGE[J]. PloS one, 2016, 11(2): e0148294,Kinoshita-Kikuta E, Kinoshita E, Eguchi Y, et al.
· Phosphopeptide Detection with Biotin-Labeled Phos-tag[J]. Phospho-Proteomics: Methods and Protocols, 2016: 17-29,Kinoshita-Kikuta E, Kinoshita E, Koike T.
· A Phos‐tag SDS‐PAGE method that effectively uses phosphoproteomic data for profiling the phosphorylation dynamics of MEK1[J]. Proteomics, 2016,Kinoshita E, Kinoshita‐Kikuta E, Kubota Y, et al.
· Difference gel electrophoresis of phosphoproteome: U.S. Patent Application 15/004,339[P]. 2016-1-22,Tao W A, Wang L.
· ERK1/2-induced phosphorylation of R-Ras GTPases stimulates their oncogenic potential[J]. Oncogene, 2016,Frémin C, Guégan J P, Plutoni C, et al.
· Microtubules Inhibit E-Cadherin Adhesive Activity by Maintaining Phosphorylated p120-Catenin in a Colon Carcinoma Cell Model[J]. PloS one, 2016, 11(2): e0148574,Maiden S L, Petrova Y I, Gumbiner B M.
· Serine 231 and 257 of Agamous-like 15 are phosphorylated in floral receptacles[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2016, 11(7): e1199314,Patharkar O R, Macken T A, Walker J C.
· A small molecule pyrazolo [3, 4-d] pyrimidinone inhibitor of zipper-interacting protein kinase suppresses calcium sensitization of vascular smooth muscle[J]. Molecular pharmacology, 2016, 89(1): 105-117,MacDonald J A, Sutherland C, Carlson D A, et al.
· The RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatase-like protein FIERY2/CPL1 interacts with eIF4AIII and is essential for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2016: TPC2015-00771-RA,Chen T, Qin T, Ding F, et al.
· Vasorelaxant Effect of 5′-Methylthioadenosine Obtained from Candida utilis Yeast Extract through the Suppression of Intracellular Ca2+ Concentration in Isolated Rat Aorta[J]. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 2016, 64(17): 3362-3370,Kumrungsee T, Akiyama S, Saiki T, et al.
· Inhibition of deubiquitinating activity of USP14 decreases tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylated at Ser19 in PC12D cells[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2016, 472(4): 598-602,Nakashima A, Ohnuma S, Kodani Y, et al.
· Actin Tyrosine-53-Phosphorylation in Neuronal Maturation and Synaptic Plasticity[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2016, 36(19): 5299-5313,Bertling E, Englund J, Minkeviciene R, et al.
· AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of lipid droplet protein PLIN2 triggers its degradation by CMA[J]. Autophagy, 2016, 12(2): 432-438,Kaushik S, Cuervo A M.
· Myocardin-related transcription factor a and yes-associated protein exert dual control in G protein-coupled receptor-and RhoA-mediated transcriptional regulation and cell proliferation[J]. Molecular and cellular biology, 2016, 36(1): 39-49,Olivia M Y, Miyamoto S, Brown J H.
· Extensive phosphorylation of AMPA receptors in neurons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(33): E4920-E4927,Diering G H, Heo S, Hussain N K, et al.
· The transmembrane region of guard cell SLAC1 channels perceives CO2 signals via an ABA-independent pathway in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2016, 28(2): 557-567,Yamamoto Y, Negi J, Wang C, et al.
· The Hippo pathway mediates inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by cAMP[J]. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 2016, 90: 1-10,Kimura T E, Duggirala A, Smith M C, et al.
· Atg13 is essential for autophagy and cardiac development in mice[J]. Molecular and cellular biology, 2016, 36(4): 585-595,Kaizuka T, Mizushima N.
· The ChrSA and HrrSA two-component systems are required for transcriptional regulation of the hemA promoter in Corynebacterium diphtheriae[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2016: JB. 00339-16,Burgos J M, Schmitt M P.
· Intergenic Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Polymorphism Upstream of rocA Alters Toxin Production and Enhances Virulence in Streptococcus pyogenes[J]. Infection and Immunity, 2016, 84(7): 2086-2093,Zhu L, Olsen R J, Horstmann N, et al.
· Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) knockout reduces fetal dysmorphogenesis in murine diabetic pregnancy[J]. Reproductive Toxicology, 2016, 62: 62-70,Ejdesjö A, Brings S, Fleming T, et al.
· Aurora kinase-induced phosphorylation excludes transcription factor RUNX from the chromatin to facilitate proper mitotic progression[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(23): 6490-6495,Chuang L S H, Khor J M, Lai S K, et al.
· Quantitative phosphoproteomics of protein kinase SnRK1 regulated protein phosphorylation in Arabidopsis under submergence[J]. Journal of experimental botany, 2016: erw107,Cho H Y, Wen T N, Wang Y T, et al.
· Temporal regulation of lipin activity diverged to account for differences in mitotic programs[J]. Current Biology, 2016, 26(2): 237-243,Makarova M, Gu Y, Chen J S, et al.
· Block of CDK1‐dependent polyadenosine elongation of Cyclin B mRNA in metaphase‐i‐arrested starfish oocytes is released by intracellular pH elevation upon spawning[J]. Molecular reproduction and development, 2016, 83(1): 79-87,Ochi H, Aoto S, Tachibana K, et al.
· Mitotic Exit Function of Polo-like Kinase Cdc5 Is Dependent on Sequential Activation by Cdk1[J]. Cell reports, 2016, 15(9): 2050-2062,Rodriguez-Rodriguez J A, Moyano Y, Játiva S, et al.
· PLK2 phosphorylates and inhibits enriched TAp73 in human osteosarcoma cells[J]. Cancer medicine, 2016, 5(1): 74-87,Hu Z B, Liao X H, Xu Z Y, et al.
· Phosphorylated TDP-43 becomes resistant to cleavage by calpain: A regulatory role for phosphorylation in TDP-43 pathology of ALS/FTLD[J]. Neuroscience research, 2016, 107: 63-69,Yamashita T, Teramoto S, Kwak S.
· The Pch2 AAA+ ATPase promotes phosphorylation of the Hop1 meiotic checkpoint adaptor in response to synaptonemal complex defects[J]. Nucleic acids research, 2016: gkw506,Herruzo E, Ontoso D, González-Arranz S, et al.
· An optimized guanidination method for large‐scale proteomic studies[J]. Proteomics, 2016,Ye J, Zhang Y, Huang L, et al.
· Expression and purification of the kinase domain of PINK1 in Pichia pastoris[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2016,Wu D, Qu L, Fu Y, et al.
· BRI2 and BRI3 are functionally distinct phosphoproteins[J]. Cellular signalling, 2016, 28(1): 130-144,Martins F, Rebelo S, Santos M, et al.
· Identification of glycoproteins associated with HIV latently infected cells using quantitative glycoproteomics[J]. Proteomics, 2016,Yang W, Jackson B, Zhang H.
· Regulation of Beclin 1 Protein Phosphorylation and Autophagy by Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and Death-associated Protein Kinase 3 (DAPK3)[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016, 291(20): 10858-10866,Fujiwara N, Usui T, Ohama T, et al.
· Regulatory Implications of Structural Changes in Tyr201 of the Oxygen Sensor Protein FixL[J]. Biochemistry, 2016, 55(29): 4027-4035,Yamawaki T, Ishikawa H, Mizuno M, et al.
· Histone demethylase Jmjd3 regulates osteoblast apoptosis through targeting anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and pro-apoptotic protein Bim[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 2016, 1863(4): 650-659,Yang D, Okamura H, Teramachi J, et al.
· Analysis of Molecular Species Profiles of Ceramide-1-phosphate and Sphingomyelin Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry[J]. Lipids, 2016, 51(2): 263-270,Yamashita R, Tabata Y, Iga E, et al.
· Highly sensitive myosin phosphorylation analysis in the renal afferent arteriole[J]. Journal of Smooth Muscle Research, 2016, 52(0): 45-55,Takeya K.
· Functional dissection of the CroRS two-component system required for resistance to cell wall stressors in Enterococcus faecalis[J]. Journal of bacteriology, 2016, 198(8): 1326-1336,Kellogg S L, Kristich C J.
· Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in vascular smooth muscle[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 2016, 310(11): C921-C930,Trappanese D M, Sivilich S, Ets H K, et al.
· ModProt: a database for integrating laboratory and literature data about protein post-translational modifications[J]. Journal of Electrophoresis, 2016, 60(1): 1-4,Kimura Y, Toda T, Hirano H.
· The C-ETS2-TFEB Axis Promotes Neuron Survival under Oxidative Stress by Regulating Lysosome Activity[J]. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2016,Ma S, Fang Z, Luo W, et al.
· Essential role of the PSI–LHCII supercomplex in photosystem acclimation to light and/or heat conditions by state transitions[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2016: 1-10,Marutani Y, Yamauchi Y, Higashiyama M, et al.
· Identification of a redox-modulatory interaction between selenoprotein W and 14-3-3 protein[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 2016, 1863(1): 10-18,Jeon Y H, Ko K Y, Lee J H, et al.
· Effects of hydrogen sulfide on the heme coordination structure and catalytic activity of the globin-coupled oxygen sensor AfGcHK[J]. BioMetals, 2016, 29(4): 715-729,Fojtikova V, Bartosova M, Man P, et al.
· Identification and functional analysis of phosphorylation in Newcastle disease virus phosphoprotein[J]. Archives of virology, 2016: 1-14,Qiu X, Zhan Y, Meng C, et al.
· Increased level of phosphorylated desmin and its degradation products in heart failure[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2016, 6: 54-62,Bouvet M, Dubois-Deruy E, Alayi T D, et al.
· Profiling DNA damage-induced phosphorylation in budding yeast reveals diverse signaling networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016: 201602827,Zhou C, Elia A E H, Naylor M L, et al.
· Unexpected properties of sRNA promoters allow feedback control via regulation of a two-component system[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016: gkw642,Brosse A, Korobeinikova A, Gottesman S, et al.
· Evolution of ZnII–Macrocyclic Polyamines to Biological Probes and Supramolecular Assembly[J]. Macrocyclic and Supramolecular Chemistry: How Izatt-Christensen Award Winners Shaped the Field, 2016: 415,Kimura E, Koike T, Aoki S.
· Phosphopeptide Enrichment Using Various Magnetic Nanocomposites: An Overview[J]. Phospho-Proteomics: Methods and Protocols, 2016: 193-209,Batalha Í L, Roque A C A.
· In vivo phosphorylation of a peptide tag for protein purification[J]. Biotechnology letters, 2016, 38(5): 767-772,Goux M, Fateh A, Defontaine A, et al.
· Regulation of cell reversal frequency in Myxococcus xanthus requires the balanced activity of CheY‐like domains in FrzE and FrzZ[J]. Molecular microbiology, 2016,Kaimer C, Zusman D R.
· Elevation of cortical serotonin transporter activity upon peripheral immune challenge is regulated independently of p38 mitogen‐activated protein kinase activation and transporter phosphorylation[J]. Journal of neurochemistry, 2016, 137(3): 423-435,Schwamborn R, Brown E, Haase J.
· The Yeast Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Routes Carbon Fluxes to Fuel Cell Cycle Progression[J]. Molecular cell, 2016, 62(4): 532-545,Ewald J C, Kuehne A, Zamboni N, et al.
· Two Degradation Pathways of the p35 Cdk5 (Cyclin-dependent Kinase) Activation Subunit, Dependent and Independent of Ubiquitination[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016, 291(9): 4649-4657,Takasugi T, Minegishi S, Asada A, et al.
· Increased level of phosphorylated desmin and its degradation products in heart failure[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports. 2016,Bouvet M, Dubois-Deruy E, Alayi T D, et al.
· a high‐affinity LCO‐binding protein of Medicago truncatula, interacts with LYK3, a key symbiotic receptor[J]. FEBS letters, 2016, 590(10): 1477-1487,Fliegmann J, Jauneau A, Pichereaux C, et al. LYR3,
· Nek1 Regulates Rad54 to Orchestrate Homologous Recombination and Replication Fork Stability[J]. Molecular Cell, 2016,Spies J, Waizenegger A, Barton O, et al.
· PhostagTM-gel retardation and in situ thylakoid kinase assay for determination of chloroplast protein phosphorylation targets[J]. Endocytobiosis and Cell Research, 2016, 27(2): 62-70,Dytyuk Y, Flügge F, Czarnecki O, et al.
· Luteinizing Hormone Causes Phosphorylation and Activation of the cGMP Phosphodiesterase PDE5 in Rat Ovarian Follicles, Contributing, Together with PDE1 Activity, to the Resumption of Meiosis[J]. Biology of reproduction, 2016: biolreprod. 115.135897,Egbert J R, Uliasz T F, Shuhaibar L C, et al.
· Newby, AC, & Bond, M.(2016). The Hippo pathway mediates inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by cAMP[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2016, 90: 1-10,Kimura-Wozniak T, Duggirala A, Smith M C, et al. G.
· Yeast lacking the amphiphysin family protein Rvs167 is sensitive to disruptions in sphingolipid levels[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2016, 283(15): 2911-2928,Toume M, Tani M.
· Regulation of CsrB/C sRNA decay by EIIAGlc of the phosphoenolpyruvate: carbohydrate phosphotransferase system[J]. Molecular microbiology, 2016, 99(4): 627-639,Leng Y, Vakulskas C A, Zere T R, et al.
· The Late S-Phase Transcription Factor Hcm1 Is Regulated through Phosphorylation by the Cell Wall Integrity Checkpoint[J]. Molecular and cellular biology, 2016: MCB. 00952-15,Negishi T, Veis J, Hollenstein D, et al.
· Validation of chemical compound library screening for transcriptional co‐activator with PDZ‐binding motif inhibitors using GFP‐fused transcriptional co‐activator with PDZ‐binding motif[J]. Cancer science, 2016, 107(6): 791-802,Nagashima S, Maruyama J, Kawano S, et al.
· ULK1/2 Constitute a Bifurcate Node Controlling Glucose Metabolic Fluxes in Addition to Autophagy[J]. Molecular cell, 2016, 62(3): 359-370,Li T Y, Sun Y, Liang Y, et al.
· Spatiotemporal dynamics of Oct4 protein localization during preimplantation development in mice[J]. Reproduction, 2016: REP-16-0277,Fukuda A, Mitani A, Miyashita T, et al.
· The tandemly repeated NTPase (NTPDase) from Neospora caninum is a canonical dense granule protein whose RNA expression, protein secretion and phosphorylation coincides with the tachyzoite egress[J]. Parasites & Vectors, 2016, 9(1): 1,Pastor-Fernández I, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Álvarez-García G, et al.
· Interaction Analysis of a Two-Component System Using Nanodiscs[J]. PloS one, 2016, 11(2): e0149187,Hörnschemeyer P, Liss V, Heermann R, et al.
· Constitutive Activation of PINK1 Protein Leads to Proteasome-mediated and Non-apoptotic Cell Death Independently of Mitochondrial Autophagy[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016, 291(31): 16162-16174,Akabane S, Matsuzaki K, Yamashita S, et al.
· p38β Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Modulates Its Own Basal Activity by Autophosphorylation of the Activating Residue Thr180 and the Inhibitory Residues Thr241 and Ser261[J]. Molecular and cellular biology, 2016, 36(10): 1540-1554,Beenstock J, Melamed D, Mooshayef N, et al.
· Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 protects against cytotoxicity induced by polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. The FASEB Journal, 2016, 30(5): 2027-2039,Akagi S, Kono N, Ariyama H, et al.
· Characterization of a herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) chimera in which the Us3 protein kinase gene is replaced with the HSV-2 Us3 gene[J]. Journal of virology, 2016, 90(1): 457-473,Shindo K, Kato A, Koyanagi N, et al.
· Generation of phospho‐ubiquitin variants by orthogonal translation reveals codon skipping[J]. FEBS letters, 2016, 590(10): 1530-1542,George S, Aguirre J D, Spratt D E, et al.
· Evolution of KaiC-Dependent Timekeepers: A Proto-circadian Timing Mechanism Confers Adaptive Fitness in the Purple Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris[J]. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(3): e1005922,Ma P, Mori T, Zhao C, et al.
· Phosphorylation of Bni4 by MAP kinases contributes to septum assembly during yeast cytokinesis[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2016, 16(6): fow060,Pérez J, Arcones I, Gómez A, et al.
· Alteration of Antiviral Signalling by Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) of Mitochondrial Antiviral Signalling Protein (MAVS)[J]. PloS one, 2016, 11(3): e0151173,Xing F, Matsumiya T, Hayakari R, et al.
· Arm-in-arm response regulator dimers promote intermolecular signal transduction[J]. Journal of bacteriology, 2016, 198(8): 1218-1229,Baker A W, Satyshur K A, Morales N M, et al.
· The lsh/ddm1 homolog mus-30 is required for genome stability, but not for dna methylation in neurospora crassa[J]. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(1): e1005790,Basenko E Y, Kamei M, Ji L, et al.
· Fine tuning chloroplast movements through physical interactions between phototropins[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016: erw265,Sztatelman O, Łabuz J, Hermanowicz P, et al.
· Characterization of the Neospora caninum NcROP40 and NcROP2Fam-1 rhoptry proteins during the tachyzoite lytic cycle[J]. Parasitology, 2016, 143(01): 97-113,Pastor-Fernandez I, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Jimenez-Ruiz E, et al.
· Transcriptional Profile during Deoxycholate-Induced Sporulation in a Clostridium perfringens Isolate Causing Foodborne Illness[J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 2016, 82(10): 2929-2942,Yasugi M, Okuzaki D, Kuwana R, et al.
· Timely Closure of the Prospore Membrane Requires SPS1 and SPO77 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Genetics, 2016: genetics. 115.183939,Paulissen S M, Slubowski C J, Roesner J M, et al.
· DDK dependent regulation of TOP2A at centromeres revealed by a chemical genetics approach[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016: gkw626,Wu K Z L, Wang G N, Fitzgerald J, et al.
· OVATE Family Protein 8 Positively Mediates Brassinosteroid Signaling through Interacting with the GSK3-like Kinase in Rice[J]. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(6): e1006118,Yang C, Shen W, He Y, et al.
· Epithelial Sel1L is required for the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis[J]. Molecular biology of the cell, 2016, 27(3): 483-490, Sun S, Lourie R, Cohen S B, et al.
· Effect of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Concentration on Supramolecular Gel Electrophoresis[J]. ChemNanoMat, 2016,Tazawa S, Kobayashi K, Yamanaka M.
· Intergenic VNTR Polymorphism Upstream of rocA Alters Toxin Production and Enhances Virulence in Streptococcus pyogenes[J]. Infection and immunity, 2016: IAI. 00258-16,Zhu L, Olsen R J, Horstmann N, et al.
· Ajuba Phosphorylation by CDK1 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Tumorigenesis[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016: jbc. M116. 722751,Chen X, Stauffer S, Chen Y, et al.
· Editorial: International Plant Proteomics Organization (INPPO) World Congress 2014[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7,Heazlewood J L, Jorrín-Novo J V, Agrawal G K, et al.
· Phosphoinositide kinase signaling controls ER-PM cross-talk[J]. Molecular biology of the cell, 2016, 27(7): 1170-1180,Omnus D J, Manford A G, Bader J M, et al.
· A multiple covalent crosslinked soft hydrogel for bioseparation[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(15): 3247-3250,Liu Z, Fan L, Xiao H, et al.
· Advances in crop proteomics: PTMs of proteins under abiotic stress[J]. Proteomics, 2016, 16(5): 847-865,Wu X, Gong F, Cao D, et al.
· Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Co-Ordinates Carbohydrate Metabolism and Cell Cycle in S. cerevisiae[J]. Molecular cell, 2016, 62(4): 546-557,Zhao G, Chen Y, Carey L, et al.
· Carbon Monoxide Gas Is Not Inert, but Global, in Its Consequences for Bacterial Gene Expression, Iron Acquisition, and Antibiotic Resistance[J]. Antioxidants & redox signaling, 2016,Wareham L K, Begg R, Jesse H E, et al.
· Two-layer regulation of PAQR3 on ATG14-linked class III PtdIns3K activation upon glucose starvation[J]. Autophagy, 2016: 1-2,Xu D, Wang Z, Chen Y.
· Regulation of sphingolipid biosynthesis by the morphogenesis checkpoint kinase Swe1[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016, 291(5): 2524-2534,Chauhan N, Han G, Somashekarappa N, et al.
· PAX5 tyrosine phosphorylation by SYK co-operatively functions with its serine phosphorylation to cancel the PAX5-dependent repression of BLIMP1: A mechanism for antigen-triggered plasma cell differentiation[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2016, 475(2): 176-181,Inagaki Y, Hayakawa F, Hirano D, et al.
· A Combined Computational and Genetic Approach Uncovers Network Interactions of the Cyanobacterial Circadian Clock[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2016: JB. 00235-16,Boyd J S, Cheng R R, Paddock M L, et al.
· HuR mediates motility of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells triggered by sphingosine 1-phosphate in liver fibrosis[J]. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2016: 1-14,Chang N, Ge J, Xiu L, et al.
· Combined replacement effects of human modified β-hexosaminidase B and GM2 activator protein on GM2 gangliosidoses fibroblasts[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2016,Kitakaze K, Tasaki C, Tajima Y, et al.
· Roseotoxin B Improves Allergic Contact Dermatitis through a Unique Anti-inflammatory Mechanism Involving Excessive Activation of Autophagy in Activated T-Lymphocytes[J]. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2016,Wang X, Hu C, Wu X, et al.
References on Phos-tag™ Chemistry
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of phosphorylated compounds using a novel phosphate capture molecule, Rapid Communications of Mass Spectrometry, 17, 2075-2081 (2003), H. Takeda, A. Kawasaki, M. Takahashi, A. Yamada, and T. Koike
-
Recognition of phosphate monoester dianion by an alkoxide-bridged dinuclear zinc (II) complex, Dalton Transactions, 1189-1193 (2004), E. Kinoshita, M. Takahashi, H. Takeda, M. Shiro, and T. Koike
-
Quantitative analysis of lysophosphatidic acid by time-of-flight mass spectrometry using a phosphate capture molecule, Journal of Lipid Research, 45, 2145-2150 (2004), T. Tanaka, H. Tsutsui, K. Hirano, T. Koike, A. Tokumura, and K. Satouchi
-
Production of 1,2-Didocosahexaenoyl Phosphatidylcholine by Bonito Muscle Lysophosphatidylcholine/Transacylase, Journal of Biochemistry,136, 477-483 (2004), K. Hirano, H. Matsui, T. Tanaka, F. Matsuura, K. Satouchi, and T. Koike
-
Novel immobilized zinc(II) affinity chromatography for phosphopeptides and phosphorylated proteins, Journal of Separation Science, 28, 155-162 (2005), E. Kinoshita, A. Yamada, H. Takeda, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, and T. Koike
-
Detection and Quantification of On-Chip Phosphorylated Peptides by Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Techniques Using a Phosphate Capture Molecule, Analytical Chemistry, 77, 3979-3985 (2005), K. Inamori, M. Kyo, Y. Nishiya, Y. Inoue, T. Sonoda, E. Kinoshita, T. Koike, and Y. Katayama
-
Phosphate-binding tag: A new tool to visualize phosphorylated proteins, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 5, 749-757 (2006), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, K. Takiyama, and T. Koike
-
Enrichment of phosphorylated proteins from cell lysate using phosphate-affinity chromatography at physiological pH, Proteomics, 6, 5088-5095 (2006), E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, E. Kinoshita, A. Yamada, M. Endo, and T. Koike
-
Separation of a phosphorylated histidine protein using phosphate affinity polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Analytical Biochemistry, 360, 160-162 (2007), S. Yamada, H. Nakamura, E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, T. Koike, and Y. Shiro
-
Label-free kinase profiling using phosphate-affinity polyacrylamide gel electrophresis, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 6, 356-366 (2007), E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, Y. Aoki, E. Kinoshita, and T. Koike
-
A SNP genotyping method using phosphate-affinity polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Analytical Biochemistry, 361, 294-298 (2007), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, and T. Koike (The phosphate group at DNA-terminal is efficiently captured by Zn2+.Phos-tag.)
-
Identification on Membrane and Characterization of Phosphoproteins Using an Alkoxide-Bridged Dinuclear Metal Complex as a Phosphate-Binding Tag Molecule, Journal of Biomolecular Techniques, 18, 278-286 (2007), T. Nakanishi, E. Ando, M. Furuta, E. Kinoshita, E. Kikuta-Kinoshita, T. Koike, S. Tsunasawa, and O. Nishimura
-
A mobility shift detection method for DNA methylation analysis using phosphate affinity polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Analytical Biochemistry, 378, 102-104 (2008), E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, E. Kinoshita, and T. Koike
-
Separation of phosphoprotein isotypes having the same number of phosphate groups using phosphate- affinity SDS-PAGE, Proteomics, 8, 2994-3003 (2008), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, M. Matsubara, S. Yamada, H. Nakamura, Y. Shiro, Y. Aoki, K. Okita, and T. Koike
-
FANCI phosphorylation functions as a molecular switch to turn on the Fanconi anemia pathway, Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 15, 1138-1146 (2008), M. Ishiai, H. Kitao, A. Smogorzewska, J. Tomida, A. Kinomura, E. Uchida, A. Saberi, E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, T. Koike, S. Tashiro, S. J. Elledge, and M. Takata
to Page top
-
Two-dimensional phosphate affinity gel electrophoresis for the analysis of phosphoprotein isotypes , Electrophoresis, 30, 550-559 (2009), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, M. Matsubara, Y. Aoki, S. Ohie, Y. Mouri, and T. Koike
-
Formation of lysophosphatidic acid, a wound-healing lipid, during digestion of cabbage leaves, Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry,73, 1293-300 (2009), T. Tanaka, G. Horiuchi, M. Matsuoka, K. Hirano, A. Tokumura, T. Koike, and K. Satouchi
-
A Phos-tag-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer system for the analysis of the dephosphorylation of phosphopeptides, Analytical Biochemistry, 388, 235-241, (2009), K. Takiyama, E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, Y. Fujioka, Y. Kubo, and T. Koike
-
Phos-tag beads as an immunoblotting enhancer for selective detection of phosphoproteins in cell lysates, Analytical Biochemistry, 389, 83-85, (2009), E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, E. Kinoshita, and T. Koike
-
Mobility shift detection of phosphorylation on large proteins using a Phos-tag SDS-PAGE gel strengthened with agarose, Proteomics, 9, 4098- 4101 (2009), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, H. Ujihara, and T. Koike
-
Separation and detection of large phosphoproteins using Phos-tag SDS-PAGE, Nature Protocols, 4, 1513-1521 (2009), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, and T. Koike
-
A clean-up technology for the simultaneous determination of lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry using a phosphate-capture molecule, Phos-tag, Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 24, 1075-1084 (2010), J. Morishige, M. Urikura, H. Takagi, K. Hirano, T. Koike, T. Tanaka, and K. Satouchi
-
Genotyping and mapping assay of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CYP3A5 using DNA-binding zinc(II) complexes, Clinical Biochemistry, 43, 302-306 (2010), E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, H. Nakashima, and T. Koike
-
The DNA-binding activity of mouse DNA methyltransferase 1 is ragulated phosphorylation with casein kinase 1σ/ε, Biochemical Journal, 427, 489-497 (2010), Y. Sugiyama, N. Hatano, N. Sueyoshi, I. Suetake, S. Tajima, E. Kinoshita, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, T. Koike, and I. Kameshita



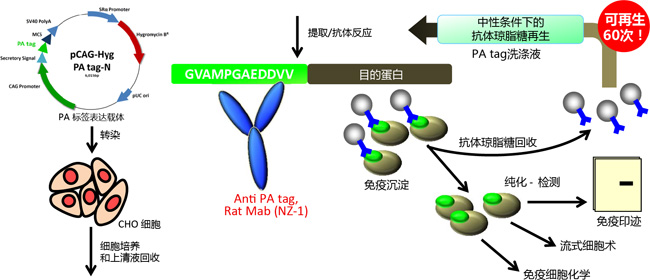
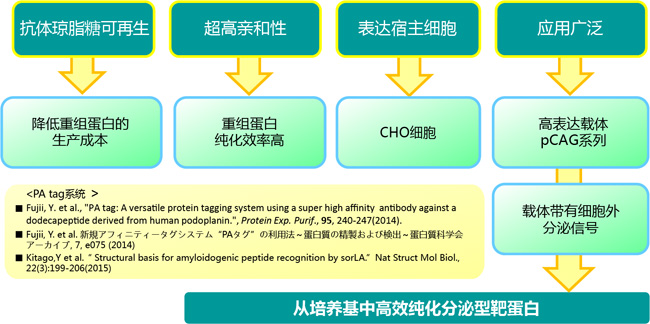
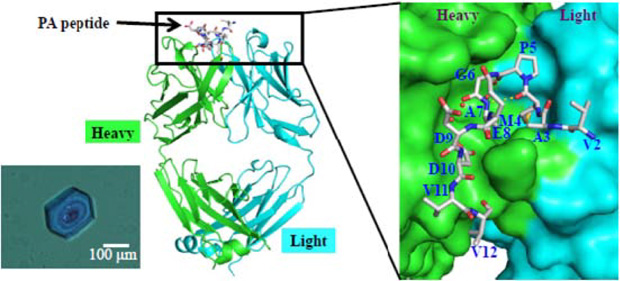


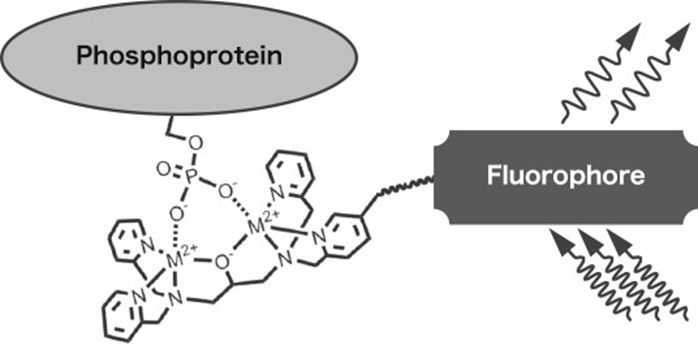
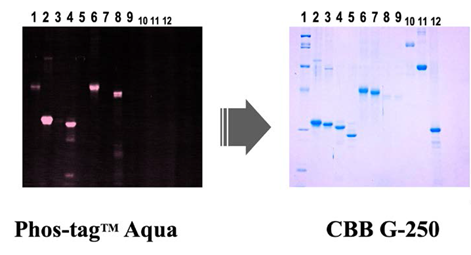
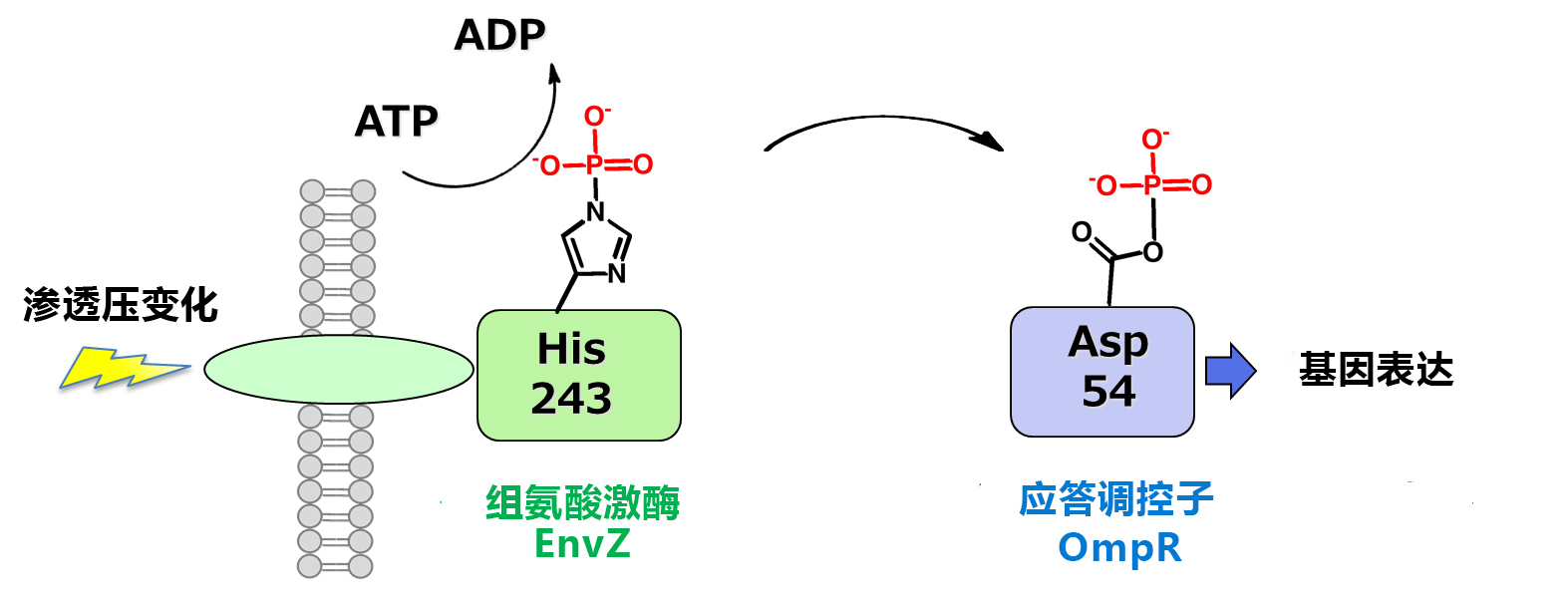
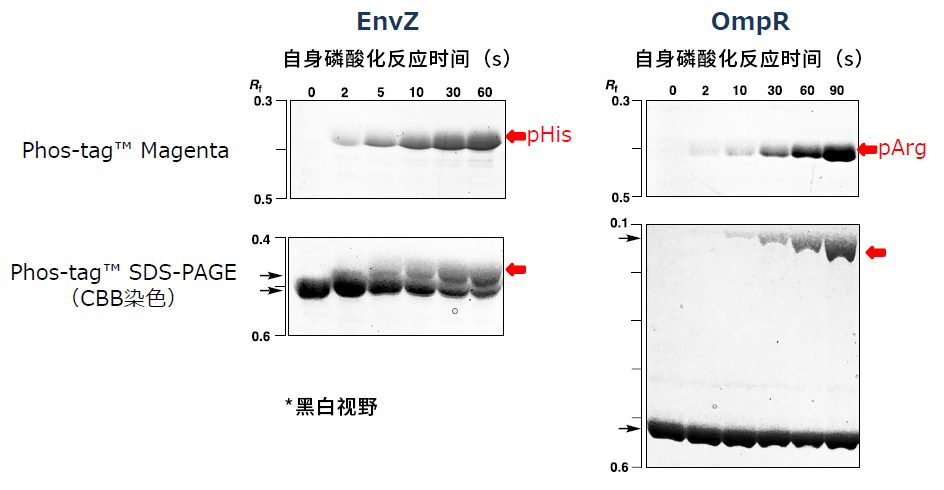
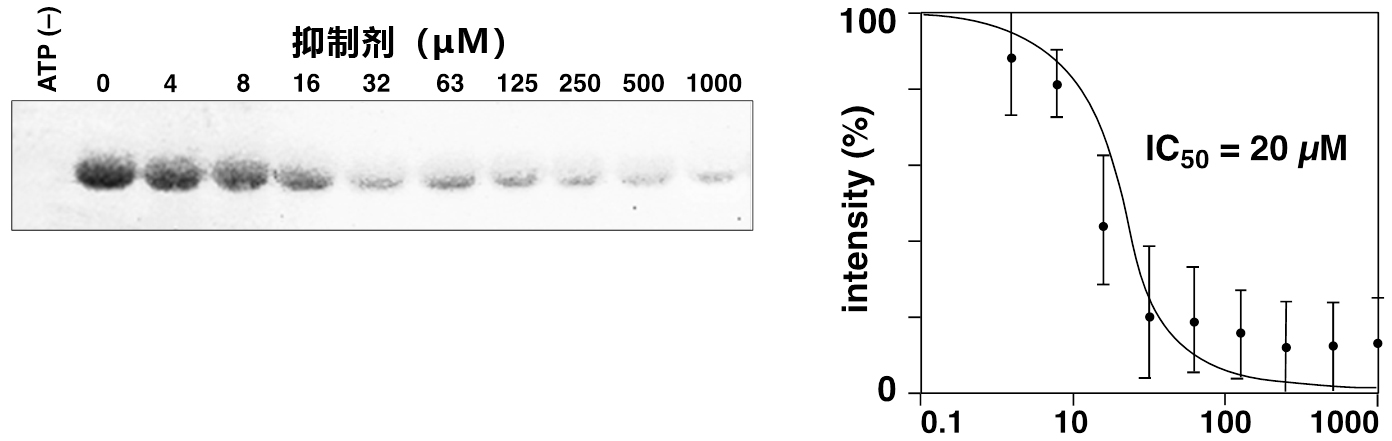
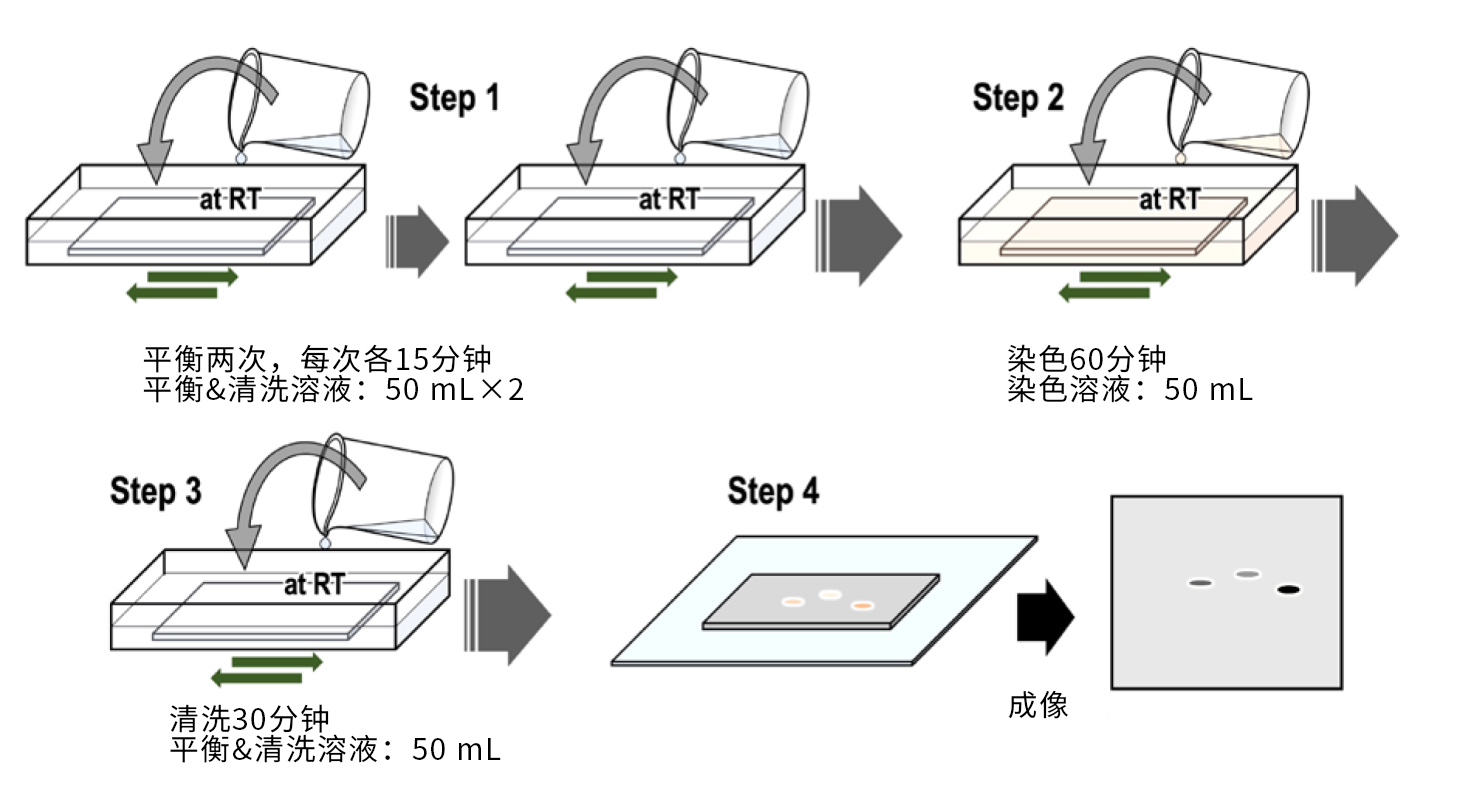



 Phos-tag
Phos-tag