上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
钙离子荧光探针Fluo-8, AM CAS 1345980-40-6
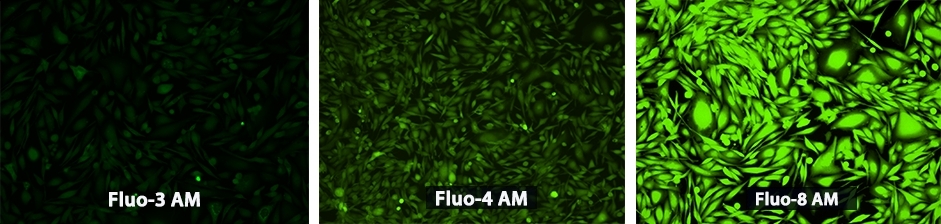 |
货号 | 21083 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 20×50 ug | 价格 | 3840 | |
| Ex (nm) | 495 | Em (nm) | 516 | |
| 分子量 | 1046.93 | 溶剂 | DMSO | |
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
钙离子荧光探针Fluo-8®, AM是美国AAT Bioquest生产的用于钙通量测定的试剂,钙通量测定是用于筛选G蛋白偶联受体(GPCR)的药物发现中的优选方法。 我们的Quest Fluo-8®和Rhod-4 系列钙检测试剂是最亮的绿色和红色钙指示剂。 我们的其他钙指标如Fluo-3,Fura-2,Indo-1,Rhod-5N和Rhod-2 AM也具有与市场上相比最高的质量,金畔生物是AAT Bioquest 的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的钙离子荧光探针。
点击查看光谱
点击查看实验方案
钙离子篇:时间轴式讲解应用于钙离子检测的探针
适用仪器
| 荧光显微镜 | |
| 激发: | FITC |
| 发射: | FITC |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明 |
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| 激发: | 490nm |
| 发射: | 525nm |
| cutoff: | 515nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明 |
| 读取模式: | 底读模式 |
产品说明书
操作步骤
1.使用钙指示剂AM Esters加载细胞:
AM酯是非极性酯,其易于穿过活细胞膜,并且通过活细胞内的细胞酯酶快速水解。 AM酯广泛用于非侵入性地将各种极性荧光探针装载到活细胞中。 但是,使用AM酯时必须小心,因为它们易于水解,特别是在溶液中。 它们应在使用前用高质量的无水二甲基亚砜(DMSO)重新配制。 DMSO储备溶液应在-20°C下干燥储存并避光。 在这些条件下,AM酯应稳定数月。
以下是我们推荐的将AM酯加载到活细胞中的方案。该方案仅提供指南,实际情况应根据您的具体需求进行修改。
a)在高质量无水DMSO中制备2至5 mM AM酯原液。
b)在实验当天,将钙指示剂溶解在DMSO中或将等份的指示剂储备溶液解冻至室温。使用0.02%Pluronic®F-127在您选择的缓冲液(如Hanks和Hepes缓冲液)中制备1至10μM的工作溶液。对于大多数细胞系,我们建议钙指示剂的最终浓度为4-5 uM。 细胞加载所需指标的确切浓度必须根据经验确定。 为避免因过载和潜在染料毒性引起的任何伪影,建议使用可产生足够信号强度的最小探针浓度。
注意:非离子洗涤剂Pluronic®F-127有时用于增加钙指示剂AM酯的水溶性。
c)如果您的细胞含有有机阴离子转运蛋白,可以在细胞培养基中加入丙磺舒(1-2.5 mM)或磺吡酮(0.1-0.25 mM),以减少脱酯化指标的泄漏。 在室温或37°C下用钙指示剂酯孵育细胞20分钟至1小时。
d)在HHBS或您选择的缓冲液(含有阴离子转运蛋白抑制剂,如2.5mM丙磺舒,如果适用)中洗涤细胞1-2次以除去过量的探针。
e)在所需的Ex / Em波长下进行实验(见说明书中的表1)。
2.测量细胞内钙响应:
为了确定溶液的游离钙浓度或单波长钙指示剂的Kd,使用以下等式:[Ca]free = Kd[F – Fmin]/Fmax – F]
其中F是实验钙水平下指示剂的荧光,Fmin是不存在钙时的荧光,Fmax是钙饱和探针的荧光。 解离常数(Kd)是探针对钙的亲和力的量度。 与校准溶液相比,荧光指示剂的Ca2 +结合和光谱性质在细胞环境中变化非常显着。 细胞内指标的原位校准通常产生显着高于体外测定的Kd值。 通过在离子载体如A-23187,4-溴A-23187和离子霉素存在下将加载的细胞暴露于受控的Ca 2+缓冲液来进行原位校准。 或者,细胞透化剂如洋地黄皂苷或X-100可用于将指示剂暴露于细胞外培养基的受控Ca2 +水平。 说明书中的表1列出了一些钙试剂的Kd值供您参考。
试剂应用文献
AMPA receptors in the synapse turnover by monomer diffusion
Authors: Morise, Jyoji and Suzuki, Kenichi GN and Kitagawa, Ayaka and Wakazono, Yoshihiko and Takamiya, Kogo and Tsunoyama, Taka A and Nemoto, Yuri L and Takematsu, Hiromu and Kusumi, Akihiro and Oka, Shogo
Journal: Nature communications (2019): 1–18
Cryo-EM Studies of TMEM16F Calcium-Activated Ion Channel Suggest Features Important for Lipid Scrambling
Authors: Feng, Shengjie and Dang, Shangyu and Han, Tina Wei and Ye, Wenlei and Jin, Peng and Cheng, Tong and Li, Junrui and Jan, Yuh Nung and Jan, Lily Yeh and Cheng, Yifan
Journal: Cell Reports (2019): 567–579
Discrimination of Dormant and Active Hematopoietic Stem Cells by G0 Marker Reveals Dormancy Regulation by Cytoplasmic Calcium
Authors: Fukushima, Tsuyoshi and Tanaka, Yosuke and Hamey, Fiona K and Chang, Chih-Hsiang and Oki, Toshihiko and Asada, Shuhei and Hayashi, Yasutaka and Fujino, Takeshi and Yonezawa, Taishi and Takeda, Reina and others
Journal: Cell Reports (2019): 4144–4158
Ketamine Increases Proliferation of Human iPSC-Derived Neuronal Progenitor Cells via Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 and Independent of the NMDA Receptor
Authors: Grossert, Aless and ra and Mehrjardi, Narges Zare and Bailey, Sarah J and Lindsay, Mark A and Hescheler, Jürgen and Saric, Tomo and Teusch, Nicole
Journal: Cells (2019): 1139
MRGPRX4 is a bile acid receptor for human cholestatic itch
Authors: Yu, Huasheng and Zhao, Tianjun and Liu, Simin and Wu, Qinxue and Johnson, Omar and Wu, Zhaofa and Zhuang, Zihao and Shi, Yaocheng and Peng, Luxin and He, Renxi and others
Journal: eLife (2019): e48431
P2Y6 signaling in alveolar macrophages prevents leukotriene-dependent type 2 allergic lung inflammation
Authors: Nagai, Jun and Balestrieri, Barbara and Fanning, Laura B and Kyin, Timothy and Cirka, Haley and Lin, Junrui and Idzko, Marco and Zech, Andreas and Kim, Edy Y and Brennan, Patrick J and others
Journal: The Journal of clinical investigation (2019)
Hyperglycaemia disrupts conducted vasodilation in the resistance vasculature of db/db mice
Authors: Lemmey, Hamish AL and Ye, Xi and Ding, Hong C and Triggle, Christopher R and Garland, Christopher J and Dora, Kim A
Journal: Vascular pharmacology (2018): 29–35
Methionine and valine activate the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 pathway through heterodimeric amino acid taste receptor (TAS1R1/TAS1R3) and intracellular Ca2+ in bovine mammary epithelial cells
Authors: Zhou, Y and Zhou, Z and Peng, J and Loor, Juan J
Journal: Journal of dairy science (2018): 11354–11363
TRPA1-dependent reversible opening of tight junction by natural compounds with an $alpha$, $beta$-unsaturated moiety and capsaicin
Authors: Kanda, Yusuke and Yamasaki, Youhei and Sasaki-Yamaguchi, Yoshie and Ida-Koga, Noriko and Kamisuki, Shinji and Sugawara, Fumio and Nagumo, Yoko and Usui, Takeo
Journal: Scientific reports (2018): 1–13
A new electro-optical approach for conductance measurement: an assay for the study of drugs acting on ligand-gated ion channels
Authors: Menegon, A and Pitassi, S and Mazzocchi, N and Redaelli, L and Rizzetto, R and Roll and JF and Poli, C and Imberti, M and Lanati, A and Grohovaz, F
Journal: Scientific Reports (2017)
Altered spontaneous calcium signaling of in situ chondrocytes in human osteoarthritic cartilage
Authors: Gong, Xiaoyuan and Xie, Wenbin and Wang, Bin and Gu, Lingchuan and Wang, Fuyou and Ren, Xiang and Chen, Cheng and Yang, Liu
Journal: Scientific reports (2017): 17093
Bystander effects elicited by single-cell photo-oxidative blue-light stimulation in retinal pigment epithelium cell networks
Authors: Ishii, Masaaki and Rohrer, Bärbel
Journal: Cell Death Discovery (2017): 16071
Bystander effects elicited by single-cell photo-oxidative blue-light stimulation in retinal pigment epithelium cell networks
Authors: Ishii, Masaaki and Rohrer, Bärbel
Journal: Cell Death Discovery (2017): 16071
High-throughput screen detects calcium signaling dysfunction in typical sporadic autism spectrum disorder
Authors: Schmunk, Galina and Nguyen, Rachel L and Ferguson, David L and Kumar, Kenny and Parker, Ian and Gargus, J Jay
Journal: Scientific Reports (2017): 40740
参考文献
Fluo-8®AM已被广泛用于研究跨越不同学科的关键生物过程中的钙离子。此类过程包括但不限于G蛋白偶联受体信号传导途径,钙离子通道活性,细胞内/细胞溶质Ca 2+通量和细胞受体的活化。
下面,您可以找到按照研究领域排序的一小部分特定Fluo-8®AM应用。如需咨询Fluo-8®AM的潜在应用,或咨询我们的荧光染料专家,请通过support@aatbio.com或1-800-990-8053与我们联系。
在肿瘤学中,Fluo-8®AM已被用于研究:
»乳腺癌细胞通过监测细胞内Ca2 +通量与细胞凋亡和2-氨基乙氧基二苯基硼酸盐的抑制作用[1]
»通过硫氧还蛋白结合蛋白2的抗肿瘤活性及其对细胞内钙浓度的依赖性 [2]
»Bcl-1和Bcl-2调节通过钙通量表征的细胞溶质转运 [3]
»Ca2 +流入和钙离子通道活性的NCI-H460细胞作为用于监测非小细胞肺癌的进展的参数 [4]
通过线粒体和内质网途径»Ca2 +释放由HN4细胞和细胞凋亡的CLIC4上调 [5]
在心脏病学,FLUO-8 ®AM已用于研究:
»低能量远场刺激作为心动过速和纤颤的治疗 [6]
»心肌细胞钙激发过程中的钙通量[7]
»心血管疾病背景下心脏传导作为细胞刚性的函数[8]
»心肌细胞中舒张期Ca2 +瞬变和SR-腔和游离细胞质Ca2 +浓度[9]
»通过细胞溶质Ca2 +通量检测唾液腺-1-磷酸(S1P)受体在瓣膜间质细胞中的活化[10]
在神经生物学中,Fluo-8®AM已被用于研究:
»海马CA1神经元,可视化神经元以研究淀粉样蛋白的作用-β在阿尔茨海默病的进展中[11]
»HEK293细胞中的细胞溶质Ca2+浓度及其对Aβ1-42和hAmylin及相关信号通路的调节作用[12]
»G蛋白偶联受体(GPRs)对突触前CA3或突触后CA1锥体细胞中大麻素的反应[13]
»延髓关于吸气爆发的中间神经元和树突状钙活性[14]
»通过细胞内Ca2+浓度的增加监测组胺激活N2a细胞[15]
在干细胞,发育和分化中,Fluo-8®AM已被用于研究:
»通过Ca2+通量和膜电位验证多能干细胞(iPSCs)诱导成功能的心肌细胞[16]
»T细胞中的CXCR4和CXCR7受体及其在细胞存活和趋化性中的作用[17]
»在Duchenne肌营养不良的发病过程中源自人诱导的多能干细胞的肌细胞对Ca2+的摄取[18]
»激动剂诱导的大鼠分化过程中的钙瞬变骨髓间充质干细胞转变为平滑肌细胞[19]
»钙通道阻滞及其对心脏祖细胞增殖和分化的影响[20]
相关产品
| 产品名称 | 货号 |
| 钙离子荧光探针Cal-520 , AM | Cat#21130 |
| 新型钙离子荧光探针Calbryte 520, AM *细胞渗透性* | Cat#20650 |
| 新型钙离子荧光探针Calbryte 590, AM *细胞渗透性* | Cat#20700 |
