上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
钙离子荧光探针Rhod-4, AM
 |
货号 | 21120 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 1 mg | 价格 | 6432 | |
| Ex (nm) | 523 | Em (nm) | 551 | |
| 分子量 | 1015.96 | 溶剂 | DMSO | |
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
产品基本信息
货号:21120
产品名称:钙离子荧光探针Rhod-4, AM
规格:1mg
储存条件:-15℃避光防潮
保质期:24个月
产品物理化学光谱特性
分子量:1015.96
溶剂:DMSO
激发波长(nm):524
发射波长(nm):551
适用仪器
| 荧光显微镜 | |
| 激发: | TRITC |
| 发射: | TRITC |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明 |
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| 激发: | 540nm |
| 发射: | 590nm |
| cutoff: | 570nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明 |
| 读取模式: | 底读模式 |
产品介绍
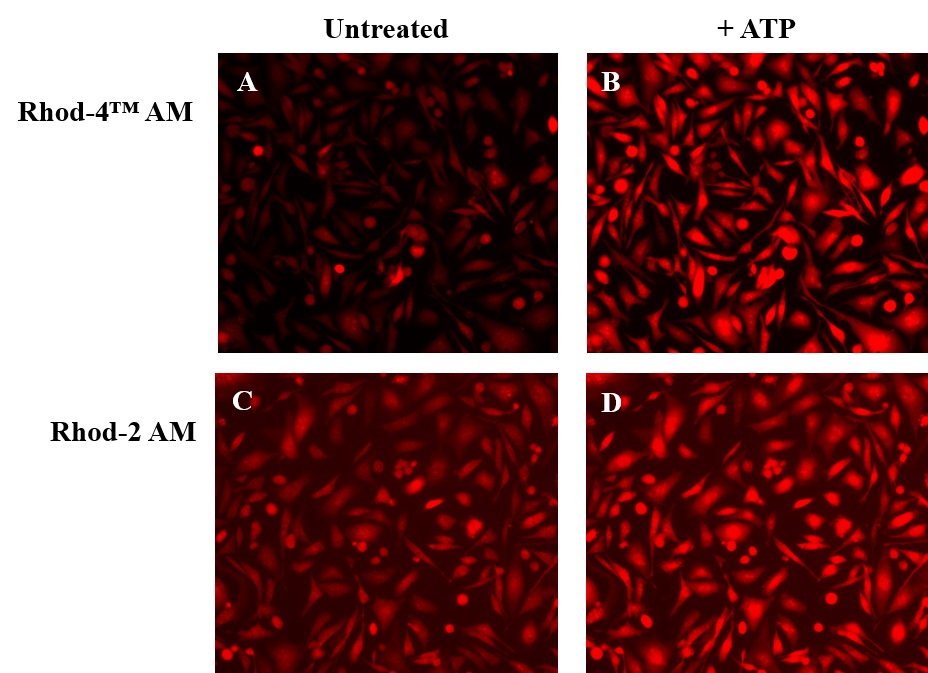
钙离子荧光探针Rhod-4, AM是美国AAT Bioquest生产的钙离子荧光探针,钙测量对于许多生物学研究至关重要。在结合Ca2+后显示光谱响应的荧光探针使研究人员能够使用荧光显微镜,流式细胞仪,荧光光谱和荧光酶标仪来研究细胞内游离Ca2+浓度的变化。在红色荧光钙指示剂中,Rhod-2最常用。但是,Rhod-2 AM在酯酶水解后仅在活细胞中呈中等荧光,并且细胞钙反应非常小。Rhod-4 的开发旨在改善Rhod-2细胞的负载和钙反应,同时保持Rhod-2的光谱波长。在CHO和HEK细胞中,Rhod-4 AM的细胞钙反应敏感性比Rhod-2 AM高10倍。AAT Bioquest提供Quest Rhod-4的多种包装大小,可满足您的特殊需求,例如1 mg;10×50 µg;20×50 µg;HTS包装,不收取额外包装费用。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的钙离子荧光探针Rhod-4, AM。
点击查看光谱
点击查看实验方案
钙离子篇:时间轴式讲解应用于钙离子检测的探针
参考文献
A high-throughput Ca2+ flux assay to monitor cyclic nucleotide-gated channel activity and characterize achromatopsia mutant channel function
Authors: Marlene A Jacobson, Laura J Jones, Dennis J Colussi, Jacqueline C Tanaka
Journal: ACS chemical neuroscience (2019)
Central role of IP 3 R2-mediated Ca 2+ oscillation in self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells elucidated by high-signal ER sensor
Authors: Cuiwei Sun, Bo Shui, Wei Zhao, Hui Liu, Wenwen Li, Jane C Lee, Robert Doran, Frank K Lee, Tao Sun, Qing Sunny Shen
Journal: Cell death & disease (2019): 396
Imaging elemental events of store-operated Ca2+ entry in invading cancer cells with plasmalemmal targeted sensors
Authors: Fujian Lu, Jianwei Sun, Qiaoxia Zheng, Jinghang Li, Yuanzhao Hu, Peng Yu, Huifang He, Yan Zhao, Xianhua Wang, Shengyu Yang
Journal: J Cell Sci (2019): jcs–224923
Manipulating energy migration within single lanthanide activator for switchable upconversion emissions towards bidirectional photoactivation
Authors: Qingsong Mei, Akshaya Bansal, Muthu Kumara Gnanasammandhan Jayakumar, Zhiming Zhang, Jing Zhang, Hua Huang, Dejie Yu, Chrishan JA Ramachandra, Derek J Hausenloy, Tuck Wah Soong
Journal: Nature Communications (2019): 1–11
Autocrine GABA signaling distinctively regulates phenotypic activation of mouse pulmonary macrophages
Authors: Luan Januzi, Jacob W Poirier, Matthew JE Maksoud, Yun-Yan Xiang, Rudolf AW Veldhuizen, Sean E Gill, Sean P Cregan, Haibo Zhang, Gregory A Dekaban, Wei-Yang Lu
Journal: Cellular Immunology (2018)
Three-dimensional model of intracellular and intercellular Ca2+ waves propagation in endothelial cells
Authors: Toshihiro Sera, Shingo Komine, Masataka Arai, Yasuhiro Sunaga, Hideo Yokota, Susumu Kudo
Journal: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2018)
Effect of stem cell niche elasticity/ECM protein on the self-beating cardiomyocyte differentiation of inducedpluripotent stem (iPS) cells at different stages
Authors: Mitsuhi Hirata, Tetsuji Yamaoka
Journal: Acta Biomaterialia (2017)
Emerin plays a crucial role in nuclear invagination and in the nuclear calcium transient
Authors: Masaya Shimojima, Shinsuke Yuasa, Chikaaki Motoda, Gakuto Yozu, Toshihiro Nagai, Shogo Ito, Mark Lachmann, Shin Kashimura, Makoto Takei, Dai Kusumoto
Journal: Scientific Reports (2017)
Preliminary findings on ultrasound modulation of the electromechanical function of human stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes
Authors: Andrew William Chen, Aleksandra Klimas, Vesna Zderic, Ivan Suares Castellanos, Emilia Entcheva
Journal: (2017): 1–4
The role of spatial organization of Ca (2+) release sites in the generation of arrhythmogenic diastolic Ca (2+) release in myocytes from failing hearts.
Authors: Andriy E Belevych, Hsiang-Ting Ho, Ingrid M Bonilla, Radmila Terentyeva, Karsten E Schober, Dmitry Terentyev, Cynthia A Carnes, Sándor Györke
Journal: Basic research in cardiology (2017): 44
