上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
线粒体膜电位荧光探针JC-10 JC-1的卓越代替品
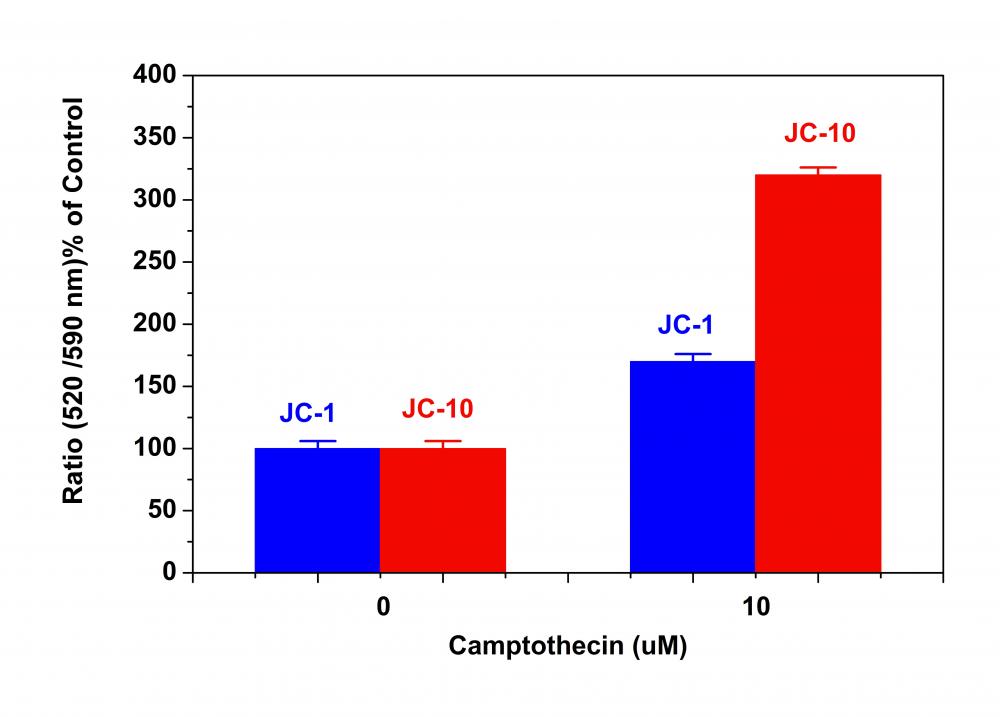 |
货号 | 22204 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 5×100 uL | 价格 | 1236 | |
| Ex (nm) | 508 | Em (nm) | 524 | |
| 分子量 | 583.34 | 溶剂 | DMSO | |
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
线粒体膜电位荧光探针JC-10是美国AAT Bioquest研发的用于检测线粒体膜电位的荧光探针是JC-1的完美替代品。JC-1在许多实验室中被广泛使用,但其水溶性差使得它在某些应用中难以使用。即使在1μM浓度下,JC-1也倾向于在水性缓冲液中沉淀。当需要高染料浓度时,JC-10已被开发为JC-1的替代物。与JC-1相比,我们的JC-10具有更好的水溶性。 JC-10能够选择性地进入线粒体,并随着膜电位的增加可逆地将其颜色从绿色变为橙色。这种性质是由于膜极化时JC-10聚集体的可逆形成导致发射光从520nm(即JC-10单体形式的发射)转变为570nm(即J-聚集体形式的发射)。当在490nm激发时,随着线粒体膜变得更加极化,JC-10的颜色从绿色橙色可逆地变为绿色橙色。使用通常安装在所有流式细胞仪中的过滤器可以检测两种颜色。可以在荧光通道1(FL1)中分析绿色发射,在通道2(FL2)中分析绿色橙色发射。除了用于流式细胞仪外,JC-10还可用于荧光成像。我们已经开发出一种在荧光微孔板平台中使用JC-10的方案。在一些细胞系中,JC-10具有优于JC-1的性能。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest 的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的线粒体膜电位荧光探针。
点击查看光谱
产品说明书
JC-10的分析方案
概述
准备含有测试化合物的细胞
添加JC-10工作溶液(100μL/孔用于96孔板或25μL/孔用于384孔板)
在室温或37 ℃孵育1小时
在Ex读取荧光强度 / Em = 490 / 525nm和540 / 590nm
注意:以下是我们推荐的活细胞方案。 该协议仅提供指南,应根据您的特定需求进行修改。
操作步骤
1.准备JC-10工作溶液:
1.1每瓶DMSO原液(100μL,2 mg / mL,3 mM)只能使用一次。任何未使用的小瓶应储存在<-20℃。注意:避免反复冻融循环,并避光.
1.2准备1X JC-10工作溶液:在实验当天,解冻一份JC-10 stockolution到室温。在Hanks和20 mM Hepesbuffer(HHBS)或您选择的缓冲液(pH 7-8,含0.02%Pluronic [表情] F-127)中制备10至30μM1X工作溶液。通过votexing将它们混合均匀。注意:对于某些细胞系,pH值为8的工作溶液可能会阻止JC-10泄漏。
2.用荧光酶标仪进行JC-10检测:
2.1用测试化合物处理细胞一段所需的时间(例如,Jurkat细胞可以用喜树碱处理4-6小时)以诱导细胞凋亡。 对于空白孔(没有细胞的培养基),加入相应量的化合物缓冲液。
2.2将100μL/孔/ 96孔板或25μL/孔/ 384孔板的JC-10工作溶液(来自步骤1.2)加入到细胞板中。
2.3将JC-10加载板在37 oC,5%CO2培养箱中孵育15-60分钟。
注意:适当的孵育时间取决于所使用的单个细胞类型和细胞浓度。优化每个实验的孵育时间。
2.4监测Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(FITC通道)和540/590 nm(TRITC通道)的荧光变化,进行比率分析。
可选:从板上取下JC-10工作溶液; 在分析之前,将100μL/孔/ 96孔板或25μL/孔/ 384孔HHBS板加回到细胞板中。
3.用荧光显微镜或流式细胞仪进行JC-10检测:
3.1用测试化合物处理细胞一段所需的时间(例如,Jurkat细胞可以用喜树碱处理4-6小时)以诱导细胞凋亡。
3.2离心细胞,每管取1-5×105个细胞。
3.3将细胞重悬于500μLJC-10工作溶液中(来自步骤1.2)。
3.4在室温或37°C,5%CO2培养箱中孵育10至30分钟,避光。
注意:适当的孵育时间取决于所使用的单个细胞类型和细胞浓度。优化每个实验的孵育时间。
3.5使用荧光显微镜(使用FITC和TRITC过滤器)或流式细胞仪(使用FL1和FL2通道)监测Ex / Em = 490/525 nm和540/590 nm处的荧光变化。可选:移除JC-10工作 从板上解决; 在荧光显微镜下分析之前,将100μL/孔/ 96孔板或25μL/孔/ 384孔HHBS板加回到细胞板中。
参考文献
JC-10™ has been used to study many biologically significant processes across several key disciplines. To list a few, JC-10™ has been used to investigate topics such as mitochondrial membrane potential, cytotoxicity, cell viability, oxidative stress, cancer metastasis, apoptosis, signal transduction, mitochondrial fission and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
Below, you may find a small sampling of specific JC-10™ applications. To inquire about a potential application of JC-10™, or to consult with our fluorescent dye specialists, please contact us at support@aatbio.com or 1-800-990-8053.
High-content assays for hepatotoxicity using induced pluripotent stem cell–derived cells.
Researchers use JC-10™ to monitor mitochondrial depolarization as an indication of hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cells, with the ultimate goal of designing a reliable, high-content and imaging-based in vitro toxicity assay.
High-Content High-Throughput Assays for Characterizing the Viability and Morphology of Human iPSC-Derived Neuronal Cultures
JC-10™ was used to study neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem-cells. Since JC-10™ will accumulate in the mitochondria of viable cells, it was used to determine cell viability in a high-throughput assay context.
Anticancer Activity of New Synthetic α-Methylene-δ-Lactones on Two Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Researchers chose JC-10™ to investigate mitochondrial membrane potential and membrane integrity in cells treated with natural products, such as α-Methylene-δ-Lactones, with the goal of developing new treatments for breast cancer.
Tetrandrine protects mouse retinal ganglion cells from ischemic injury.
JC-10™ was used in flow cytometry to study mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) in primary cultured retinal ganglion cells, as an extension of the field of drug discovery into prevention of ischemic injury.
Midazolam induces cellular apoptosis in human cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in xenograft mice
In a study of human cancer cells, JC-10™ was employed to track cellular apoptosis as a function of mitochondrial membrane potential, and consequently, mitochondrial activity. Researchers were interested in the possible anesthetic properties of midazolam for anticancer drug delivery.
Mitochondrial proteomics with siRNA knockdown to reveal ACAT1 and MDH2 in the development of doxorubicin-resistant uterine cancer
JC-10™ was used by researchers for the purposes of drug discovery. In particular, researchers were interested in finding new treatments for doxorubicin-resistant uterine cancer, using JC-10™ to monitor mitochondrial membrane potential and validate cell viability results.
Cold exposure lowers energy expenditure at the cellular level
Researchers used JC-10™ to investigate the relationship between temperature and cellular activity. In particular, researchers wanted to explore if cold temperature acts as a stressor on mitochondrial membrane potential, with regards to the oxidative phosphorylation process which generates ATP.
Susceptibility of gametes and embryos of the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, to Karenia brevis and its toxins
JC-10™ was used in the study of sperm viability, fertilization successs and embryonic survival of Crassostrea virginica. Specifically, JC-10™ was used to quantify mitochondrial membrane potential in sperm cells and to determine possible toxicity effects of algal blooms.
Calmodulin antagonists induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vitro and inhibit tumor growth in vivo in human multiple myeloma
JC-10™ was used by researchers to study cell cycle and apoptosis in human multiple myeloma. JC-10™ functioned as a probe for the detection of mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization, which was crucial to the study of caspase activated apoptosis.
Activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway produces reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in hepatocytes that contribute to liver tumorigenesis
Researchers were interested in the pathways involved with liver tumorigenesis. To that end, they used JC-10™ to study activation of apoptotic pathways related to changes in mitochondrial membrane potential, with the ultimate goal of discovering if antioxidant therapy might help suppress liver carinogenesis.
